Setup and Optimize the National Instruments PXI-5441 Waveform Generator
The National Instruments PXI-5441 is a powerful PXI waveform generator designed to support high-speed waveform downloads up...

As the new school year starts, there are classrooms full of engineering students who do not remember the time before the use of both Wi-Fi and Bluetooth was commonplace. These technologies did not become widely available to the public until the early 2000s, but given their prevalence within everyday life in 2022, it is clear that these short-range communication networks are catalysts for innovation. With so much technological advancement in such a short amount of time, it’s worth asking the question- how did we get here, and what does the future look like?
How Does it Work?
Wi-Fi utilizes radio waves that operate at certain frequencies to send data between devices, routers, and other equipment. Choosing the right frequency, either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, depends on how much data has to be transferred. In general, there are two types of wireless Wi-Fi networks: infrastructure and ad hoc.
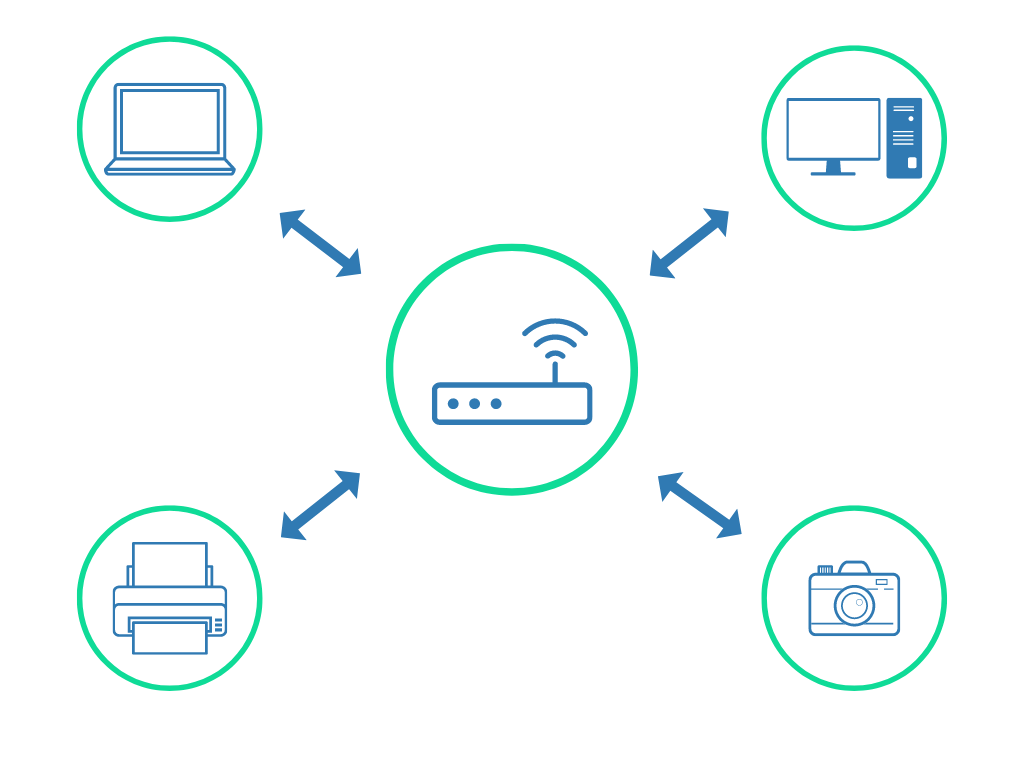
In an infrastructure network, data is sent between wireless devices after first going through a centralized wireless network router or hotspot access point (AP). This network configuration is most commonly used in homes and hotspots.
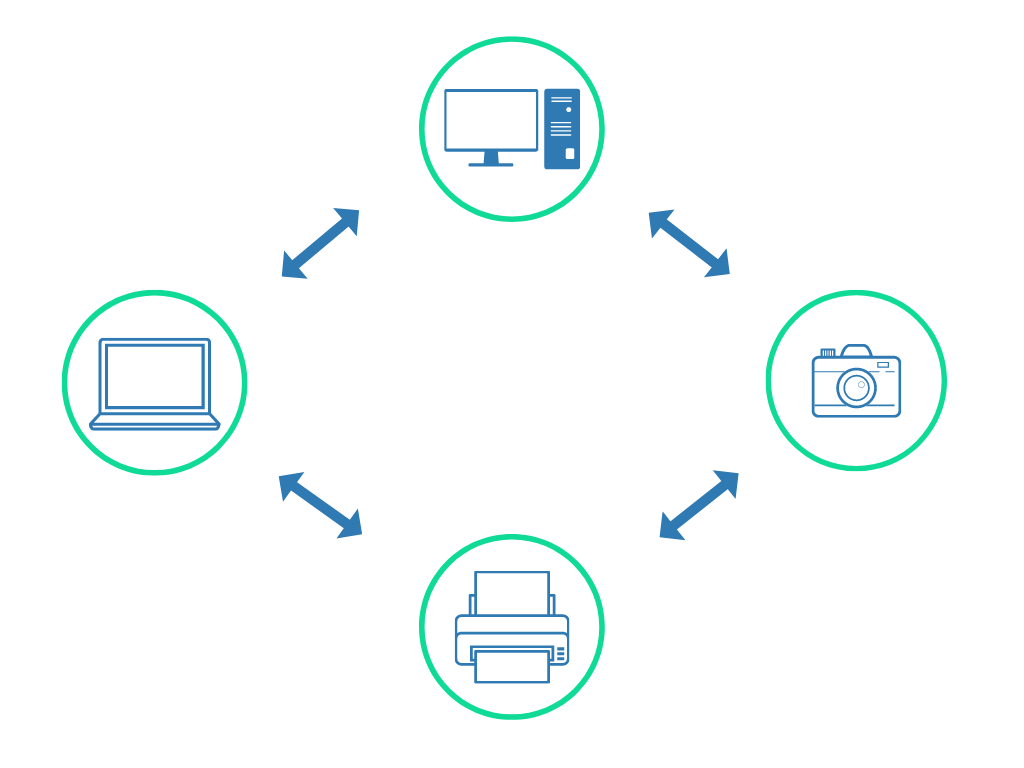
In an ad hoc network, data is shared directly between the different devices that are on the shared network without having to first go through an AP. The term “ad hoc” means to be used “when necessary or needed”, which perfectly describes this network’s ability to bypass a central / wireless access point.
Advantages of Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is capable of connecting multiple types of devices, both to each other and to the internet. The use of Wi-Fi in public places has increased exponentially since the first citywide Wi-Fi service in the USA began in Sunnyvale, CA in 2005. As a result, basically all laptops and smartphones come with wireless network adapters, which results in effortless connection.
Products can be “Wi-Fi Certified”, which means that they have successfully completed the interoperability certification training provided by the Wi-Fi Alliance. Even standard Wi-Fi devices that are certified can function anywhere, and the products are backwards compatible.
Wi-Fi networks are also capable of enhancing security and protection for data through WPA2s (Wi-Fi protected access encryption).
What Comes Next?
Wi-Fi CERTIFIED 6, the most recent version of Wi-Fi connection, is based on the IEEE 802.11ax standard and offers increased range, improved performance in crowded areas, and improved battery economy for devices. With billions of people using Wi-Fi every day, speed and reliability are top concerns. Upcoming revisions to Wi-Fi will no doubt focus on higher throughput for data, increasing data transmission rates, and reducing congestion.

How Does it Work?
Bluetooth is a Personal Area Network (PAN), which means that it can be used to connect devices that are within close proximity to one another (usually within 10 m), or to connect a device to the internet. Bluetooth technology uses radio waves from the 2.4 to 2.485 GHz band to connect devices (laptops, headsets, keyboards, etc.) using transmitters and receivers.
The Bluetooth transmitter sends input data through a filter known as the Gaussian frequency shift keying (GFSK) filter at a rate of 1 MHz. This filter smooths out pulses of the signal, with a 500 KHz cutoff frequency. The signal then goes through a wideband filter, and then to the antennae.
The Bluetooth receiver receives the signal, which is down-converted from being a high-frequency signal to an IF frequency (ideally 110.6 MHz).
Advantages of Bluetooth
Bluetooth technology has an incredible range of applications. While it does not have the same range as Wi-Fi signals, it allows for wireless control and communication between devices such as smartphones and headsets or car stereos. The wireless communication transmission of audio that Bluetooth provides a better alternative to FM transmissions.
Bluetooth has replaced the need for RS-232 as a means of wired serial communication in the industries of test equipment, medical equipment, GPS receivers, and more.
Personal security has also greatly benefitted from Bluetooth technology. Real-time location systems (RTLS) can use “nodes” and “tags” to track objects in real time and find their precise location, and security on mobile phones can help prevent theft and loss..
What Comes Next?
One of the most prominent markets for Bluetooth enabled devices is wearable smart tech. Gadgets such as smartwatches, hearing aids, Fit Bits, and more are not only making connectivity more convenient, but changing how we approach our day to day lives. Health sensor devices can send data to a smartphone app or other device, increasing awareness and independence. In the next few years, Bluetooth enabled wearables will make up a sizable percentage of the market.
Additional Information:
https://www.wi-fi.org/
https://www.bluetooth.com/
A monthly email packed with valuable content—industry news, tutorials, obsolescence updates, and more. No sales pitches, just insights we think you'll find helpful!
The National Instruments PXI-5441 is a powerful PXI waveform generator designed to support high-speed waveform downloads up...
Companies in almost every industry are being transformed by artificial intelligence, and autonomous machines are...
The PXIe Platform from National Instruments offers an incredibly valuable toolset for test and measurement innovation. Its...
It is no secret that simulation and testing is an important part of designing circuits....